LangGraph: Callbacks vs. Middleware in v1 - what’s the difference?
TL;DR
Use callbacks when you want to observe what’s happening (logging, tracing, streaming tokens). Use middleware when you want to shape behavior (modify requests/responses, enforce policy, or alter control flow like short‑circuiting or jumping back to the model/tools).
What each is designed for
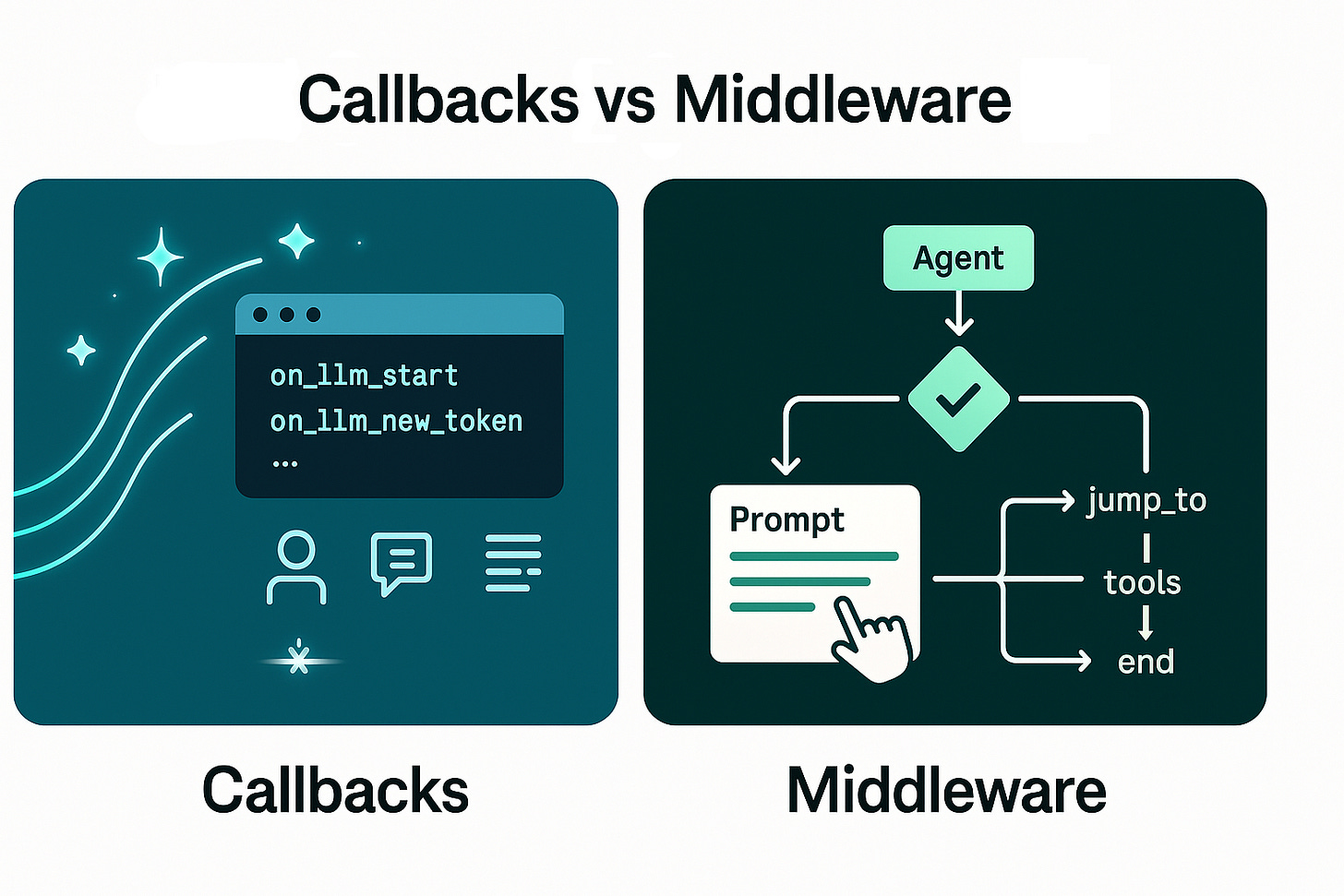
Callbacks: A lightweight, event-based mechanism that emits lifecycle events from models, tools, chains/runnables. Ideal for observability tasks such as logging, token streaming, usage tracking, debugging, and tracing. You attach handlers at request time or construction time and they propagate through child runnables. See the official list of events (e.g.,
on_llm_start,on_llm_new_token,on_chain_end) in the callbacks docs. Reference.Middleware (v1): A first-class, ordered pipeline for agents that can read and mutate state, modify model/tool requests and responses, and even change execution flow (e.g., “jump to tools”, “jump back to model”, or “end”). It’s intended for cross-cutting behavioral logic like rewriting prompts, adding guardrails, human-in-the-loop checkpoints, summarization, or caching strategies. Reference.
Key differences at a glance
Primary goal
Callbacks: Observability and side effects (log, trace, stream).
Middleware: Behavioral control (mutate inputs/outputs, enforce policy), plus observability if you want.
Where they attach
Callbacks: On any Runnable/model/tool via the
callbacksargument (request-time) or constructor; propagates to children (with async caveats).Middleware: On the v1 agent runtime as ordered middleware; executes in sequence around model and tool nodes.
Mutation/control
Callbacks: Generally not intended to change inputs/outputs or control flow; they’re event notifications.
Middleware: Can modify state, requests, and responses; can exit early or “jump” within the agent (e.g.,
jump_to: “model” | “tools” | “end”).
Execution order
Callbacks: Handlers are invoked when events fire; primarily reactive.
Middleware: Deterministic chain-of-responsibility; earlier middleware can short‑circuit so later ones don’t run.
Built-ins
Callbacks: N/A (pattern-oriented; lots of ecosystem handlers exist).
Middleware: Summarization, Human-in-the-loop, Anthropic prompt caching, Dynamic system prompt.
Async propagation note
Callbacks: In Python ≤3.10, async custom runnables may need manual callback propagation to children.
Middleware: No special caveat called out beyond standard agent middleware ordering/jumps.
Typical uses
Callbacks: Logging, token streaming to UIs, LangSmith tracing, metrics, debugging.
Middleware: Safety/policy checks, prompt augmentation, dynamic routing, tool gating, early exit, memory injection, human approvals.
When to use which
Choose callbacks if you need to observe or emit events with minimal coupling: logging, counting tokens, streaming tokens to a UI, or tracing runs across models/tools/chains.
Choose middleware if you need to intervene: rewrite prompts, add/strip tools, conditionally bypass a step, inject state, enforce guardrails, or add human-in-the-loop approvals.
Can I use both?
Yes. Middleware governs behavior and flow at the agent level, while callbacks continue to emit events from models, tools, and other runnables. It’s common to rely on middleware for behavioral policy and callbacks for observability/telemetry.
Real-world examples
Callbacks
Logging and metrics
from typing import Any
from langchain.callbacks.base import BaseCallbackHandler
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
class MetricsHandler(BaseCallbackHandler):
def __init__(self) -> None:
self.token_count = 0
def on_llm_new_token(self, token: str, **kwargs: Any) -> None:
self.token_count += 1
def on_llm_end(self, response: Any, **kwargs: Any) -> None:
print(f”Total tokens streamed: {self.token_count}”)
llm = ChatOpenAI(model=”gpt-4o-mini”)
_ = llm.invoke(”Summarize LangChain callbacks in two sentences.”,
config={”callbacks”: [MetricsHandler()]})Live token streaming to a console/UI
from typing import Any
from langchain.callbacks.base import BaseCallbackHandler
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
class StreamPrinter(BaseCallbackHandler):
def on_llm_new_token(self, token: str, **kwargs: Any) -> None:
print(token, end=”“, flush=True)
llm = ChatOpenAI(model=”gpt-4o-mini”)
_ = llm.invoke(”Explain retrieval-augmented generation briefly.”,
config={”callbacks”: [StreamPrinter()]})Middleware (v1)
Summarization middleware for long chats
from langchain.agents import create_agent
from langchain.agents.middleware import SummarizationMiddleware
agent = create_agent(
model=”openai:gpt-4o”,
tools=[...],
middleware=[
SummarizationMiddleware(
model=”openai:gpt-4o-mini”,
max_tokens_before_summary=4000,
messages_to_keep=20,
)
],
)Human-in-the-loop approvals for sensitive tools
from langchain.agents import create_agent
from langchain.agents.middleware import HumanInTheLoopMiddleware
from langgraph.checkpoint.memory import InMemorySaver
hitl = HumanInTheLoopMiddleware(
tool_configs={
“write_file”: {”allow_accept”: True, “allow_edit”: True},
“execute_sql”: {”allow_accept”: True},
}
)
agent = create_agent(
model=”openai:gpt-4o”,
tools=[...],
middleware=[hitl],
checkpointer=InMemorySaver(), # required for interrupts
)Early-exit policy with jump_to
from typing import Any
from langchain.agents.middleware import AgentMiddleware, AgentState
from langchain.agents import create_agent
class SafetyMiddleware(AgentMiddleware):
def before_model(self, state: AgentState) -> dict[str, Any] | None:
last_msg = state[”messages”][-1].content.lower()
if “delete all” in last_msg:
return {
“messages”: [{”role”: “assistant”, “content”: “Operation blocked by policy.”}],
“jump_to”: “end”,
}
return None
agent = create_agent(
model=”openai:gpt-4o”,
tools=[...],
middleware=[SafetyMiddleware()],
)Notes
The callbacks docs you’ll find today are under the 0.x line and note deprecation alongside LangChain v1.0; the concepts still map as an event system for observability. Callbacks.
Middleware documented in the v1‑alpha OSS docs includes explicit control‑flow primitives like
jump_toand a catalog of built-ins for common behaviors. Middleware in v1.
References
Callbacks: https://python.langchain.com/docs/concepts/callbacks/
Middleware in v1 (Python): https://docs.langchain.com/oss/python/langchain/middleware